Difference between startup capital and working capital
This post will cover ‘working capital’, ‘startup capital’, and ‘startup loans’ and help you distinguish between the three.
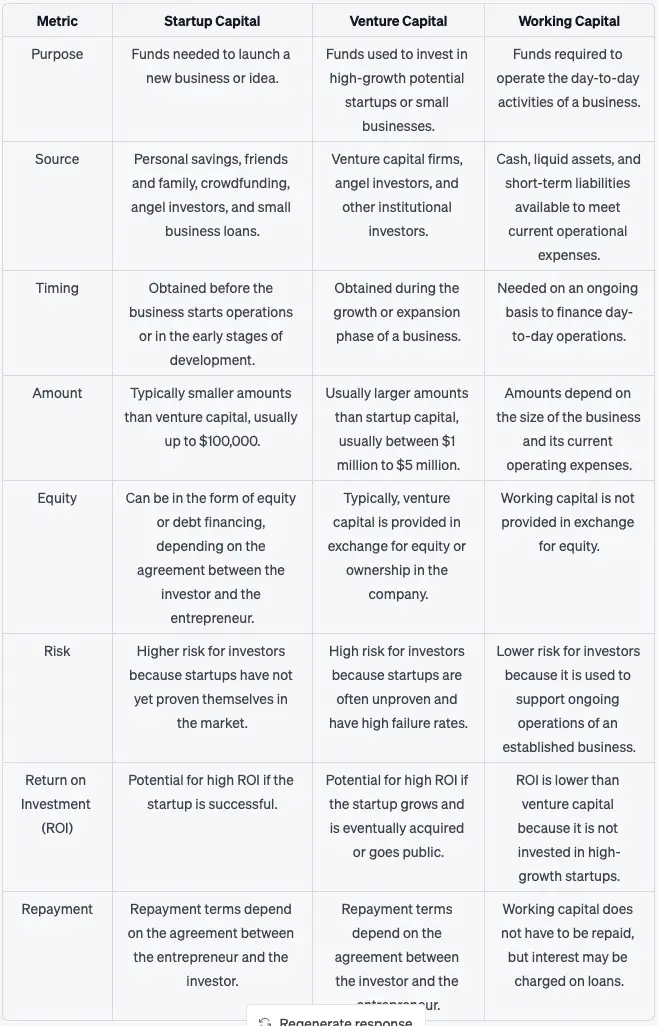
Financial analysts must frequently make a distinction between working capital and startup capital in the course of their work.
Working capital also referred to as net-working capital or NWC, describes the difference between an organization’s current assets (e.g., cash, inventory, accounts receivable) and its current liabilities (e.g., accounts payable). Working capital is a tool for assessing a company’s cash flow.
Startup capital, on the other hand, is a monetary investment in a corporation for the purposes of product growth, production, expansion, brand management, office space, and inventory. The funds raised by a new company to fund its initial costs are referred to as startup capital. This money gives runway to the startups & helps spend on necessary expenses like salaries, product development, marketing, etc.
If you are a startup founder raising venture capital for your business, use our venture capital funding tool to find out if your startup is venture fundable and how you can increase your chances of raising money from angel investors and VC firms.
What is Working Capital?
Working capital is a short-term predictor of a company’s operating performance, liquidity, and financial health.
If a business has sufficient positive working capital, it can theoretically expand and invest with the funds available.
When an organization’s current assets are less than its current liabilities, it can have trouble repaying creditors or incurring expenses. Furthermore, the company could go bankrupt.
Working capital is measured by subtracting the company’s existing assets from its current liabilities, as previously stated.
The financial obligations of a company that are due and payable within a year are known as current liabilities. These are displayed on a company’s website. Current assets are assets that are expected to be liquidated or converted into cash in less than a year. Current liabilities must also be paid within a year.
Working capital is needed for most major ventures, such as expanding into new markets or increasing output. It has a negative effect on the company’s cash flow. However, if sales rates are falling or money is being received slowly, the cash level will fall, resulting in a similar drop in accounts receivable.
What is Startup Capital?
Startup capital is the initial capital required to run a startup business smoothly.
This capital can be from entrepreneurs’ own pockets, from their family & friends, or even from external investors like business angels and venture capitalists.
Startups are young businesses that are still in the early stages of growth. These businesses are started by one or more individuals who want to create and sell a product or service.
One of the first things a startup has to do is raise funds. Most people refer to this form of funding as “startup money” or “venture capital”.
Entrepreneurs use startup capital to cover most or all of the costs associated with starting a new company.
This involves paying for initial hires, office space, permits, licenses, inventory, market analysis, testing, product production, and marketing, as well as any other costs.
In certain situations, a new venture will need more than one round of startup capital funding to get off the ground.
Professional investors such as venture capitalists and/or angel investors offer the bulk of startup funding to young companies. Banks and other financial institutions can also provide startup capital to certain businesses.
It’s no surprise that businesses can receive large sums of money from their investors, given the sources of startup funding.
Since investing in young companies is risky, these investors often demand a solid business plan in return for their investment. In return for their contribution, they typically receive a share of the company’s ownership.
As a business grows and is put on the market, it is common to seek startup capital in multiple funding rounds.
The final round could be an initial public offering (IPO), in which the company raises enough money to reward its investors while also investing in the company’s future growth.
Don’t forget to take some of our interesting business quizzes that will help you make great decisions:
- Do you have founder market fit?
- What is your entrepreneur burnout level?
- Business name quiz – Do you have the right name for your business?
- Is it time to pivot your startup?
- Quiz to find out if you need a business mentor
- Quiz to find out if you’re working with the right mentor
What about startup loans?
Startup loans are a form of debt capital and have to be paid back to the lender.
For expanding their operations, small businesses are increasingly turning to online business loans and funding options.
Flexi EMIs and quick short-ticket financing are two advantages that online lenders have over commercial banks.
As a result, non-banking financial institutions have become the preferred choice for modern SMEs.
Non-banking financial institutions are currently allocating working capital loans and unsecured business loans across the country, while banks are restricting their commercial lending activities.
At different stages of your company’s development, both of these are critical.
We’ll focus on start-up capital and working capital in this article.
You’ll need money to keep your company afloat while it gets up and running.
What would you do with your money?
- Payroll and its associated costs (for you and any employees)
- Utilities (phones, electricity, Internet, and communications, among other things)
- Rent
- Marketing and sales-related expenses
- Taxes on supplies, maintenance, and insurance
Make sure you budget enough money for the true costs of running your company during the first year of operations. (Also, remember to pay yourself first!)
Make sure you’ve budgeted for more workers, increased production, more supplies for those new hires, and so on.
One of the most common reasons for new businesses failing is a lack of sufficient start-up capital. (Another factor is inept management.)
Forecast your financial needs reasonably and give space for the unforeseen, or you may find yourself out of business.
Here are some of the reasons why you should apply for a business loan from a Non-Bank Financial Institution (NBFC):
1. Timely Turnaround
The timely availability of financing is the one factor that determines its significance.
If you do not obtain the necessary funds within the time frame specified, the opportunity will be missed, or the same activity will cost you more.
Because the majority of small business owners apply with them, banks scrutinize business loan applications at their leisure. As a result, the loan approval process is lengthy.
NBFCs, on the other hand, specialize in financing small businesses. As a result, they complete documentation, verification, and disbursements in a timely manner.
2. Process is conducted entirely online.
The company’s online-only loan application process is one of the reasons why NBFCs would approve loans faster.
Digital copies of required loan verification documents (in India) like PAN, Aadhar Card, Bank Statements, and ITR Certifications are available to every modern company.
Where banking institutions grapple with filing and manual paperwork, an online lender can quickly check your company’s statutory status and disburse loans.
3. Only the bare minimum of documentation is required.
The lender can check your business and personal information through government online portals an online process, so there is no need to submit a lot of paperwork and papers.
NBFCs provide business loans by checking only the essential documents for your company’s identity, address, incorporation, and tax compliance.
4. Payments that are flexible
Lenders can cut costs associated with manual work by using an entirely online business loan process, and they are delighted to pass those savings on to you.
When you get a business loan from an online lender like Lendingkart Finance, you can expect lower business loan interest rates, more flexible EMI options, and lower processing fees.
Difference between working capital and a startup loan?
Working capital is the money that a business has available to meet its short-term obligations, such as inventory, accounts payable, and payroll. A startup loan is a type of business loan that helps new businesses get off the ground by providing them with the funding they need to cover initial expenses and operating costs.
There are a few key differences between working capital and a startup loan.
- First, working capital is typically used to finance day-to-day operations, while a startup loan is generally used to fund the initial costs of starting a business.
- Second, working capital is typically repaid within a shorter time frame than a startup loan.
- Finally, working capital is often easier to obtain than a startup loan, as it is typically less risky for lenders.
If you’re a new business owner, you may be wondering how to raise the working capital you need to get your business up and running. There are a few different options to consider, such as loans, credit cards, and personal savings. Keep in mind that each option has its own set of pros and cons, so be sure to weigh your options carefully before making a decision.
One option for raising working capital is to take out a loan. There are a number of different types of loans available to businesses, including SBA loans, lines of credit, and term loans. Each type of loan has its own set of terms and conditions, so be sure to compare your options before choosing a loan.
Another option for raising working capital is to use credit cards. Credit cards can be a great way to finance small purchases or cover unexpected expenses. However, it’s important to keep in mind that credit cards typically have high interest rates, so you’ll need to be careful about how much you charge.
Finally, you can also use personal savings to finance your business. This option can be a good choice if you have the resources available and you’re comfortable taking on the risk. However, it’s important to keep in mind that using personal savings to finance your business can put your personal finances at risk.
No matter which option you choose, be sure to carefully consider your options before making a decision. Raising working capital is an important part of starting a new business, so be sure to choose the option that’s right for you.
Difference between working capital and growth capital
There is a big difference between working capital and growth capital. Growth capital is used to finance a company’s expansion, whereas working capital is used to finance a company’s day-to-day operations.
Growth capital is typically larger in amount than working capital, and it is also more long-term in nature. Working capital, on the other hand, is typically smaller in amount and more short-term in nature.
Another key difference between working capital and growth capital is that working capital is mostly generated internally by a company, while growth capital is mostly sourced externally from investors.
So, if you’re wondering how to raise working capital, the answer really depends on what you need the capital for. If you need it for short-term operational purposes, then you can generate it internally from your company’s operations. However, if you need it for long-term expansion purposes, then you will need to source it externally from investors.
Check out some of our related posts below:
- How to calculate burn rate & cash runway for your startup?
- Do you need a data room for your startup?
- Why contribution margin is a strong predictor of company success?
- The Keys to Successful Startup Due Diligence: A Complete Guide for founders & investors
- What are the different business startup costs and how to reduce them?
FAQ: Working Capital and Startup Capital
Q: What is working capital? A: Working capital refers to the short-term financial resources that a company has available to cover its day-to-day operational expenses, such as inventory, accounts payable, and payroll. It is a measure of a company’s liquidity and financial health.
Q: Why is working capital important? A: Working capital is crucial for a company’s operations and growth. It allows the business to meet its short-term obligations, invest in new opportunities, and navigate through financial challenges. Insufficient working capital can lead to difficulties in repaying creditors, incurring expenses, and even bankruptcy.
Q: How is working capital calculated? A: Working capital is calculated by subtracting a company’s current liabilities from its current assets. Current liabilities are the financial obligations due within a year, while current assets are assets expected to be converted into cash within a year.
Q: What is startup capital? A: Startup capital refers to the initial capital required to launch and establish a new business venture. It includes the funds needed to cover various expenses associated with starting a company, such as hiring employees, renting office space, obtaining permits and licenses, conducting market analysis, and producing and marketing products or services.
Q: Where can startup capital come from? A: Startup capital can come from various sources, including the entrepreneur’s personal savings, contributions from family and friends, and external investors such as business angels or venture capitalists. Additionally, banks and non-banking financial institutions can provide startup loans to certain businesses.
Q: How do startup loans differ from working capital? A: Startup capital and working capital serve different purposes. Startup capital is used to cover the initial costs of starting a business, while working capital is used to finance ongoing operational expenses. Startup capital is typically obtained at the early stages of a business, while working capital is needed throughout a company’s lifespan.
Q: How can I raise working capital for my business? A: There are several options for raising working capital, such as taking out a loan from banks or non-banking financial institutions, utilizing business credit cards, or using personal savings. Each option has its pros and cons, so it’s important to carefully consider which option suits your business’s needs and financial situation.
Q: What is the difference between working capital and growth capital? A: Working capital is used to finance day-to-day operational needs, while growth capital is used to fund a company’s expansion and long-term growth initiatives. Working capital is typically generated internally from a company’s operations, while growth capital is often sourced externally from investors.
Q: Where can I find investors for startup capital? A: To secure startup capital from investors, you can approach angel investors, venture capitalists, or even consider going public through an initial public offering (IPO). Angel investors are individuals or organizations that invest in startups in exchange for ownership equity or convertible debt. Venture capitalists provide funding to startups in exchange for an ownership stake. Going public allows a company to raise capital by selling shares to the public.
Q: How can I ensure I have enough startup capital and working capital? A: It is crucial to conduct thorough financial planning and budgeting to determine the amount of startup capital and working capital your business needs. Consider all the necessary expenses, such as payroll, utilities, rent, marketing, and taxes. It’s also important to leave room for unforeseen expenses and unexpected challenges. By forecasting your financial needs accurately, you can ensure you have sufficient capital to support your business’s growth and operations.
Parting Words
To conclude, money for investment capital must come from somewhere in both cases.
A new business can pursue funding from a variety of sources, including angel investors.
An angel investor is an individual or organization that invests in a startup company in return for ownership equity or convertible debt. They may make a one-time or ongoing investment to help the business get through its early stages. The funds will be used to develop and market the company’s products.
When a new company goes public, it is obtaining large amounts of capital from a variety of investors.
A company can be funded in a variety of ways.
Instead of focusing on how to finance, one should consider what type of expenditure is being made before deciding on the best way to fund it.
To summarize, equity should be used to fund startup costs.
Working capital is almost always financed with short-term debt. When a company is generating revenue or has assets, it can also be financed by debt capital.
Make sure to check out our blog, for more such gems of information, as we take full pride in our intentions to enrich our readers with the knowledge to successfully run their own startup.